Problem, research strategy, and findings:
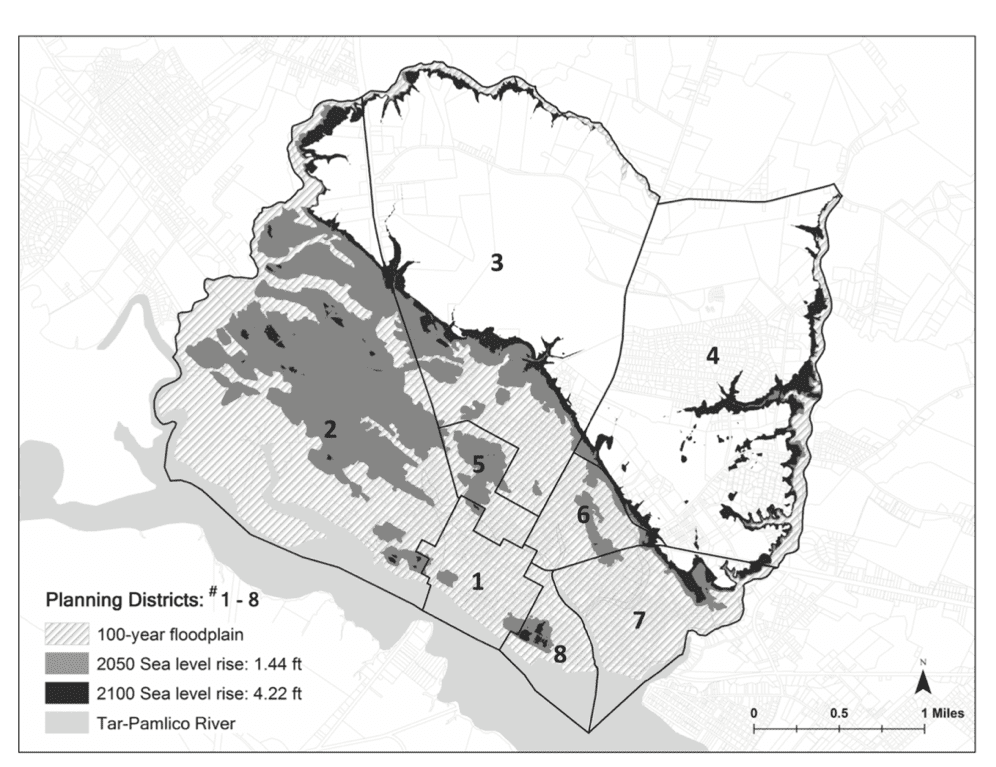
Land use planning is key to mitigating natural hazards and the effects of climate change. Communities adopt multiple plans that directly and indirectly address hazard mitigation; the integration of local plans can significantly affect future community vulnerability to hazards. We develop a resilience scorecard to assess the degree to which the network of local plans targets areas most prone to hazards and then evaluate the coordination of local plans and test it in Washington (NC), a community vulnerable to coastal floods and projected sea-level rise. We find that local plans are not fully consistent and do not always address the areas in a community most vulnerable to floods or sea level risks; moreover, some plans actually increase physical and social vulnerability to hazards. While these results indicate the validity of a resiliency scorecard, we were forced to use a narrow range of vulnerability indicators; better data would improve the process.
Takeaway for practice:
Planners can assume a crucial role in improving planning for hazards by using the scorecard to identify conflicts among local plans, assessing whether local plans target areas most vulnerable to specific hazards. Planners can inform the public and decision makers about missed opportunities to improve local hazard mitigation planning. To support such important efforts, the U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency and other federal agencies should consider developing additional databases that are widely applicable and available.
FROM P. 292

